Throughout its history, the Earth has experienced many extinction events that have resulted in the demise of innumerable species. These extinction eras have left behind a rich fossil record and influenced the direction of evolution. This article will discuss some of the significant extinction events and the creatures who survived them.
The 485–443 million-year Ordovician Period
Marine life underwent major diversity throughout the Ordovician Period. During this period, arthropods, called trilobites, dominated the animal kingdom. Protofish, cephalopods, and brachiopods were among the other noteworthy creatures.
The 419–359 million-year Devonian Period
Different fish species evolved throughout the Devonian Period, often referred to as the Age of Fishes. Oceans were home to placoderms and the ancestors of sharks, which were jawed fish. Around this same period, the first amphibians appeared and adapted to both aquatic and terrestrial habitats.
The 299–252 million-year Permian Period.
Reptile diversity increased throughout the Permian Period. During this period, synapsids—a class of reptiles that eventually gave origin to mammals—were quite common. The main land animals were a subset of synapsids called therapsids. But the Permian Period also saw the greatest mass extinction catastrophe in Earth’s history, the Permian-Triassic extinction event, which eliminated around 70% of terrestrial vertebrate species and 96% of marine species.
The 145–66 million-year Cretaceous Period
Dinosaurs are the main reason for the fame of the Cretaceous Period. During this period, dinosaurs dominated the landscape; modern humans find themselves enthralled by dinosaur species such as Tyrannosaurus rex, Triceratops, and Velociraptor. Many aquatic reptiles, such as plesiosaurs and mosasaurs, lived in the water.
The 2.6 million–11,700-year Pleistocene Epoch
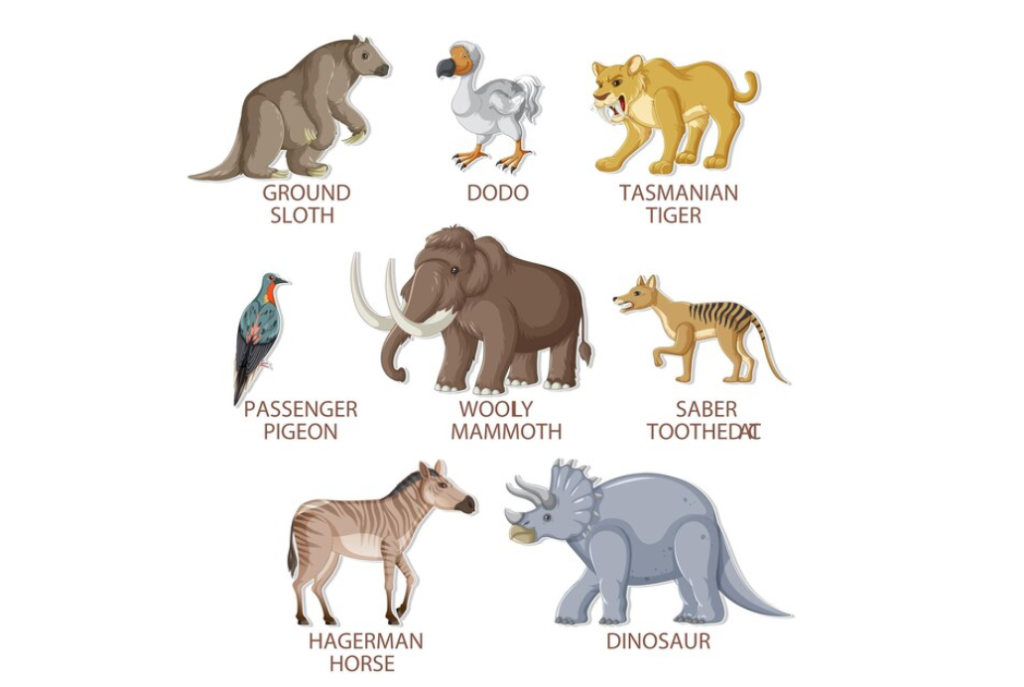
Big animals were prevalent during the Pleistocene Epoch, sometimes referred to as the Ice Age. Saber-toothed cats, enormous ground sloths, and woolly mammoths were among the legendary creatures that once roamed the planet. But many of these megafauna became extinct around the end of the Pleistocene, maybe as a result of a mix of hunting by humans and climatic change.
Numerous animal species have come and gone throughout the history of our planet. Although the process of extinction has been happening naturally for millions of years, human activity has recently increased the pace at which species are becoming extinct. This article will discuss creatures that became extinct at various points in Earth’s history.
1. Extinctions in the Prehistoric Era
The Earth was home to a wide variety of unusual and intriguing animals before humans ever existed. Saber-toothed tigers, woolly mammoths, and dinosaurs are a few of the most well-known extinct species from this era. Approximately 66 million years ago, during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, these species became extinct.
2. The Holocene Extinctions
The present geological era is known as the Holocene epoch, which started around 11,700 years ago. Many species have become extinct throughout this period owing to a variety of circumstances, such as habitat loss, hunting, and climate change. The dodo bird, which was indigenous to the island of Mauritius and became extinct in the 17th century as a result of human activity, is one famous example.
3. Modern Extinctions
Many species have gone extinct in more recent times as a result of human activity. The passenger pigeon, which was once among the most common birds in North America, is one well-known example. But in the early 20th century, overhunting and habitat degradation caused it to become extinct.
The thylacine, or Tasmanian tiger, is another sad example. Native to Tasmania and the Australian mainland, this unusual mammal was driven to extinction in the early 20th century by habitat degradation and poaching.
4. Endangered Species
Many species are now threatened with extinction, while others have already become extinct. To preserve the survival of these endangered species, urgent conservation activities are needed. The Hawksbill sea turtle, Sumatran orangutan, and black rhinoceros are a few instances of endangered species.
Global governments and conservation groups are attempting to save these animals and their natural environments. The prevention of further extinctions depends heavily on initiatives like legislation, breeding programs, and wildlife sanctuaries.